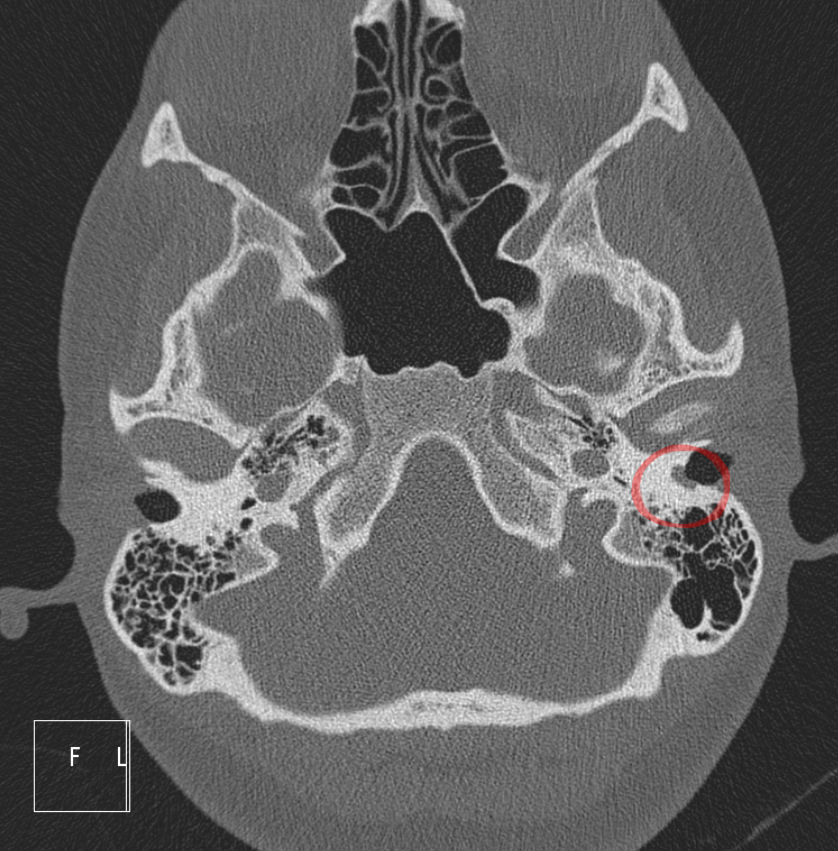
What is a Cholesteatoma?
A cholesteatoma is an abnormal growth occurring in the middle ear comprised of keratin (skin cells). Left untreated, the growth can enlarge and disrupt the function of the middle ear bones, leading to hearing loss.
Causes
A cholesteatoma is caused by aggressive skin growth often in response to ear trauma, surgery, chronic ear infection, a retraction of the skin into the middle ear, or as a congenital condition. Excess skin growth in the middle ear can cause bone erosion and recurring ear infections.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a cholesteatoma include:
- spinning sensation or dizziness (vertigo)
- temporary or permanent hearing loss
- ringing in the ear (tinnitus)
- pressure/fullness of the ear
- facial paralysis
- discharge from the ear and ear infections
Treatment
Cholesteatomas can be diagnosed by observation with an otoscope, CT scan, and hearing test audiograms. Once diagnosed, treatment entails the surgical removal of the skin growth. Follow up is necessary to ensure that the growth does not return and occasional ear cleaning by a healthcare professional may be needed. Secondary surgeries can occur if the growth is not fully removed or returns after an initial surgery.
Symptoms such as excess drainage and ear infections caused by a cholesteatoma can be treated with antibiotic drops and medications.